Table Of Content
Is the period effect in the first square the same as the period effect in the second square? If it only means order and all the cows start lactating at the same time it might mean the same. But if some of the cows are done in the spring and others are done in the fall or summer, then the period effect has more meaning than simply the order. Although this represents order it may also involve other effects you need to be aware of this. A Case 3 approach involves estimating separate period effects within each square. The Greek letters each occur one time with each of the Latin letters.
Statistical Methods for Data Science
If the experimenter focuses exclusively on the differences between treatments, the effects due to variations between the different blocks should be eliminated. Interpretation of the coefficients of the corresponding models, residualanalysis, etc. is done “as usual.” The only difference is that we do not test theblock factor for statistical significance, but for efficiency. Instead of a single treatment factor, we can also have a factorial treatmentstructure within every block. When I analyze the fertilizer, I have 32 experimental units (the thing I have applied my treatment to), but when analyzing the effect of irrigation, I only have 8 experimental units. A non-blocked way to run this experiment would be to run each of the twelve experimental wafers, in random order, one per furnace run. That would increase the experimental error of each resistivity measurement by the run-to-run furnace variability and make it more difficult to study the effects of the different dosages.
2 Split-plot designs
This is a Case 2 where the column factor, the cows are nested within the square, but the row factor, period, is the same across squares. The simplest case is where you only have 2 treatments and you want to give each subject both treatments. Here as with all crossover designs we have to worry about carryover effects. This property has an impact on how we calculate means and sums of squares, and for this reason, we can not use the balanced ANOVA command in Minitab even though it looks perfectly balanced. We will see later that although it has the property of orthogonality, you still cannot use the balanced ANOVA command in Minitab because it is not complete.
2.4 Evaluating and Choosing a Blocking Factor
The error is more dependent on the specific conditions that exist for performing the experiment. For instance, if the protocol is complicated and training the operators so they can conduct all four becomes an issue of resources then this might be a reason why you would bring these operators to three different factories. It depends on the conditions under which the experiment is going to be conducted. The numerator of the F-test, for the hypothesis you want to test, should be based on the adjusted SS's that is last in the sequence or is obtained from the adjusted sums of squares. That will be very close to what you would get using the approximate method we mentioned earlier.
Other Aspects of the RCBD
For a complete block design, we would have each treatment occurring one time within each block, so all entries in this matrix would be 1's. For an incomplete block design, the incidence matrix would be 0's and 1's simply indicating whether or not that treatment occurs in that block. The dataset oatvar in the faraway library contains information about an experiment on eight different varieties of oats. Within each block, the researchers created eight plots and randomly assigned a variety to a plot.

3.7 Reference Designs
If we want to analyze data from an RCBD, we need to assume that the block-by-treatment interaction is negligible. We can then merge the interaction and residual factors and use the sum of their variation for estimating the residual variance (Fig. 7.2D). We continue with our example of how three drug treatments in combination with two diets affect enzyme levels in mice. To keep things simple, we only consider the low fat diet for the moment, so the treatment structure only contains Drug with three levels. Our aim is to improve the precision of contrast estimates and increase the power of the omnibus \(F\)-test.
Design of Experiments with R. Building 2^k Factorial Designs by Roberto Salazar - Towards Data Science
Design of Experiments with R. Building 2^k Factorial Designs by Roberto Salazar.
Posted: Tue, 03 Dec 2019 05:32:29 GMT [source]
Therefore we partition our subjects by gender and from there into age classes. Thus we have a block of subjects that is defined by the combination of factors, gender and age class. In this case, we would have four rows, one for each of the four varieties of rice. In this case, we have five columns, one for each of the five blocks. In each block, for each treatment, we are going to observe a vector of variables. This kind of design is used to minimize the effects of systematic error.
A detailed microstructural and multiple responses analysis through blocking design to produce Ca(II)-alginate beads ... - ScienceDirect.com
A detailed microstructural and multiple responses analysis through blocking design to produce Ca(II)-alginate beads ....
Posted: Sun, 26 Sep 2021 06:19:24 GMT [source]
Book traversal links for 4.1 - Blocking Scenarios
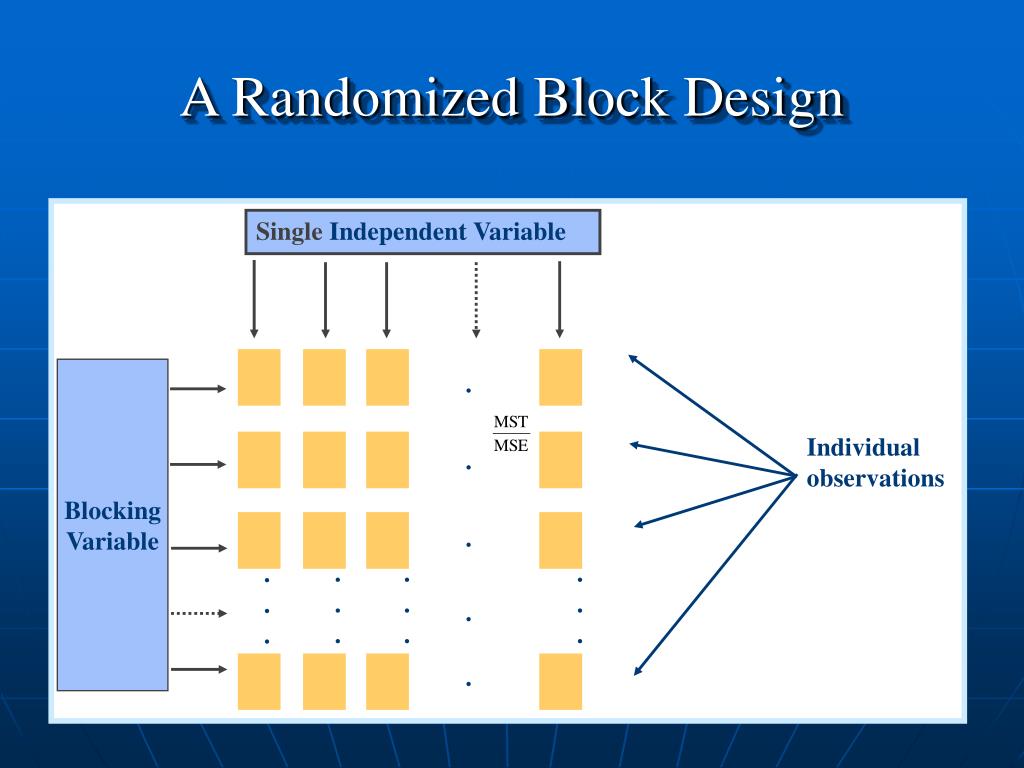
Randomized block design still uses ANOVA analysis, called randomized block ANOVA. When participants are placed into a block, we anticipate them to be homogeneous on the control variable, or the blocking variable. In other words, there should be less variability within each block on the control variable, compared to the variability in the entire sample if there were no control variable. Less within-block variability reduces the error term and makes estimate of the treatment effect more robust or efficient, compared to without the blocking variable. Several blocking factors can be combined in a design by nesting—allowing estimation of each blocking factor’s contribution to variance reduction—or crossing—allowing simultaneous removal of several independent sources of variation.
The department has particular strength in Machine Learning, a key ingredient of the emerging field of Data Science. It is also very useful to combine studies of statistics and probability with other subjects. Our department excels at interdisciplinary science, and more than half of the department's undergraduate students are double or triple majors. We note that the sum of squares and the mean square estimates are slightly larger than for the aov() analysis, because the between-block information is taken into account. This provides more power and results in a slightly larger value of the \(F\)-statistic.
For instance, if you had a plot of land the fertility of this land might change in both directions, North -- South and East -- West due to soil or moisture gradients. As we shall see, Latin squares can be used as much as the RCBD in industrial experimentation as well as other experiments. Without the blocking variable, ANOVA has two parts of variance, SS intervention and SS error. All variance that can't be explained by the independent variable is considered error. By adding the blocking variable, we partition out some of the error variance and attribute it to the blocking variable.
Once the data are recorded, we are interested in quantifying how ‘good’ the blocking performed in the experiment. This information would allow us to better predict the expected residual variance for a power analysis of our next experiment and to determine if we should continue using the blocking factor. The omnibus \(F\)-test for the treatment factor provides clear evidence that the drugs affect the enzyme levels differently and the differences in average enzyme levels between drugs is about 85 times larger than the residual variance. Situations where you should use a Latin Square are where you have a single treatment factor and you have two blocking or nuisance factors to consider, which can have the same number of levels as the treatment factor. This is a simple extension of the basic model that we had looked at earlier. The row and column and treatment all have the same parameters, the same effects that we had in the single Latin square.
Essentially, this fully crosses the latin square with a new blocking factor and leads to the model specification y ~ drug + Error(rep+device+tech) or y ~ drug + (1|rep) + (1|device) + (1|tech) for Figure 7.15F. Linear mixed models and ‘traditional’ analysis of variance use the same linear model to analyze data from a given design. Their main difference is the way they handle models with multiple variance components. Linear mixed models use different techniques for estimation of the model’s parameters that make use of all available information. Variance estimates are directly available, and linear mixed models do not suffer from problems with unbalanced group sizes. Colloquially, we can say that the analysis of variance approach provides a convenient framework to phrase design questions, while the linear mixed model provides a more general tool for the subsequent analysis.
This design allows us to fully remove thebetween-block variability, e.g., variability between different locations, fromthe response because it can be explained by the block factor. In that sense, blocking is a so-calledvariance reduction technique. It is straightforward to extend an RCBD from a single treatment factor to factorial treatment structures by crossing the entire treatment structure with the blocking factor.

No comments:
Post a Comment